Encephalitis
Does the patient have a penicillin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Non-severe immediate or delayed penicillin hypersensitivity
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Severe immediate or delayed penicillin hypersensitivity
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) BUT DOES NOT INCLUDE other life-threatening reactions
such as Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug
reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis. If your
patient has a history of these, contact infectious diseases for advice
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Empiric encephalitis treatment
In any patient with suspected acute encephalitis with no penicillin allergy give:
Aciclovir 10 mg/kg (child 12 years or younger: 500
mg/m2) intravenously, 8-hourly
AND if the patient is an adult at risk of Listeria monocytogenes
infection (see below) ADD:
Benzylpenicillin 2.4 g intravenously, 4-hourly
Code for IV aciclovir is:
3enc
This code is valid for THREE days only, starting from the
first day of treatment for this condition. Infectious diseases must be contacted if treatment is to
continue past 72 hours. Please annotate this code on the medication chart and document when
infectious diseases are to be contacted in the patient notes.
- If the patient has any signs of meningism (nuchal rigidity, photophobia and headache) treat
as per meningitis. If the diagnosis of meningitis vs encephalitis is unclear, treat for BOTH
- Diagnostic tests for encephalitis should include analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), serum, respiratory samples and faecal samples, as well as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and electroencephalogram (EEG)
- For management of neonates and children with possible L. monocytogenes infection, seek expert advice
- Patients at risk of Listeria infection include: neonates and patients who are older than 50
years, immunocompromised, pregnant or debilitated, or those with a history of hazardous alcohol
consumption
- Aciclovir should be started in all patients with suspected acute encephalitis while further
investigations are underway, because herpes simplex virus (HSV) is the most common treatable cause
- Use the online calculator in the Therapeutic Guidelines Antibiotic to calculate body surface area in children
- A dose of 500 mg/m2 is approximately equal to 20 mg/kg for children younger than 5 years
and 15 mg/kg for children 5 years to 12 years
- Herpes simplex encephalitis can usually be excluded and empirical therapy stopped based on negative
CSF nucleic acid amplification tests (eg polymerase chain reaction [PCR]) and a normal MRI. However,
tests for herpes simplex virus in CSF can be negative in very early disease (before day 3 of
illness); consider a repeat lumbar puncture and PCR if clinical suspicion is high
References:
See section on encephalitis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Empiric encephalitis treatment
In any patient with suspected acute encephalitis with a penicillin allergy give:
Aciclovir 10 mg/kg (child 12 years or younger: 500
mg/m2) intravenously, 8-hourly
AND if the patient is an adult at risk of Listeria monocytogenes
infection (see below) ADD:
Trimethoprim+sulfamethoxazole 5+25 mg/kg up to 480+2400 mg intravenously, 8-hourly
Code for IV aciclovir and IV trimethoprim+sulfamethoxazole is:
3enc
This code is valid for THREE days only, starting from the
first day of treatment for this condition. Infectious diseases must be contacted if treatment is to
continue past 72 hours. Please annotate this code on the medication chart and document when
infectious diseases are to be contacted in the patient notes.
- If the patient has any signs of meningism (nuchal rigidity, photophobia and headache) treat
as per meningitis. If the diagnosis of meningitis vs encephalitis is unclear, treat for BOTH
- Diagnostic tests for encephalitis should include analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), serum, respiratory samples and faecal samples, as well as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and electroencephalogram (EEG)
- For management of neonates and children with possible L. monocytogenes infection, seek expert advice
- Patients at risk of Listeria infection include: neonates and patients who are older than 50
years, immunocompromised, pregnant or debilitated, or those with a history of hazardous alcohol
consumption
- Aciclovir should be started in all patients with suspected acute encephalitis while further
investigations are underway, because herpes simplex virus (HSV) is the most common treatable cause
- Use the online calculator in the Therapeutic Guidelines Antibiotic to calculate body surface area in children
- A dose of 500 mg/m2 is approximately equal to 20 mg/kg for children younger than 5 years
and 15 mg/kg for children 5 years to 12 years
- Herpes simplex encephalitis can usually be excluded and empirical therapy stopped based on negative
CSF nucleic acid amplification tests (eg polymerase chain reaction [PCR]) and a normal MRI. However,
tests for herpes simplex virus in CSF can be negative in very early disease (before day 3 of
illness); consider a repeat lumbar puncture and PCR if clinical suspicion is high
References:
See section on encephalitis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Neonatal herpes simplex infection treatment
Please follow the flow chart below:
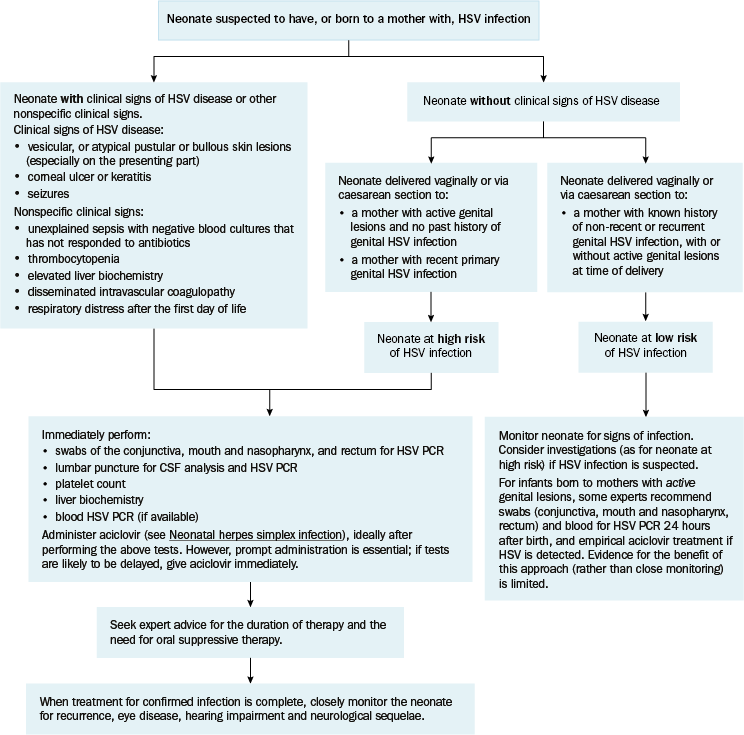
Image taken from the Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019. Section on Neonatal Herpes Simplex Infection
If patient requires treatment for herpes simplex infection give:
Aciclovir 20 mg/kg intravenously, 8-hourly
Code for IV aciclovir is:
2neh
This code is valid for TWO days only, starting from the
first day of treatment for this condition. Infectious diseases must be contacted if treatment is to
continue past 48 hours. Please annotate this code on the medication chart and document when
infectious diseases are to be contacted in the patient notes.
- In neonates, infection with herpes simplex virus (HSV) can present with isolated skin or mucous membrane lesions, encephalitis, pneumonitis or disseminated infection. Management is complex and expert advice is required. Please contact infectious diseases immediately for advice on treatment and management
- The duration of treatment depends on the clinical presentation. Disease affecting the skin, eyes and mouth requires 14 days of intravenous therapy. At least 21 days of intravenous therapy is required for neonates with disseminated disease or encephalitis. Treatment for encephalitis should continue until herpes simplex virus is no longer detected in the cerebrospinal fluid—seek advice from infectious diseases
- The role and duration of therapy in high-risk asymptomatic neonates has not been fully established. The risk to the neonate is related to whether the mother’s herpes simplex virus infection is primary and within 6 to 10 weeks of delivery (higher risk) or recurrent (much lower risk). Examples of higher-risk asymptomatic neonates include:
- neonates with negative herpes simplex virus polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, but who are born either via vaginal tract or caesarean section to mothers with primary herpes simplex virus active genital lesions at the time of delivery
- neonates with positive herpes simplex virus PCR swabs (from the conjunctiva, mouth and nasopharynx, or rectum) who are born to mothers with a history of recurrent herpes simplex virus infection
- Some experts recommend 10 days of antiviral therapy (as above) for these infants
- Oral aciclovir should not be used for initial treatment of herpes simplex virus infection in neonates. However, there is evidence for oral suppressive therapy (after completion of the intravenous treatment course) to prevent neurological recurrence following encephalitis in neonates. Suppressive therapy with oral aciclovir can also be considered in preterm neonates (to prevent early reactivation of disease) and in term neonates who have skin, eye or mouth lesions (to prevent cutaneous recurrence). Suppressive therapy is usually continued for at least 6 months. Seek expert advice
- After successful treatment, monitor all infants closely for recurrence of herpes simplex virus infection. If recurrence occurs, seek expert advice
- For more comprehensive information, see the Australasian Society for Infectious Diseases (ASID) guidelines Management of Perinatal Infections
References:
See section on neonatal herpes simplex infection - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Penetrating Eye Injury
Following penetrating eye injury please start prophylaxis with:
Moxifloxacin 400 mg (child: 10 mg/kg up to 400 mg) orally, daily for 5 to 7 days
OR if moxifloxacin is not available
Ciprofloxacin 750 mg (child: 20 mg/kg up to 750 mg) orally, twice daily for 5 to 7 days
Following surgical repair, consider adding topical therapy
Ciprofloxacin 0.3% eye drops, 1 drop into the affected eye, four times a day for 7 days
OR
ofloxacin 0.3% eye drops, 1 drop into the affected eye, four times a day for 7 days
OR (if available)
Cefazolin 5% plus gentamicin 0.9% eye drops, 1 drop into the affected eye, four times a day for 7 days
OR (if there is a low risk of endophthalmitis)
Chloramphenicol 0.5% eye drops, 1 drop into the affected eye, four times a day for 7 days
Code for ciprofloxacin or moxifloxacin PO is:
7pen
This code is valid for SEVEN days only, starting from the
first day of treatment for this condition. Infectious diseases must be contacted if treatment is to
continue past one week. Please annotate this code on the medication chart and document when
infectious diseases are to be contacted in the patient notes.
- Do not use topical antibiotics if an open globe injury is suspected because preservatives are toxic to the intraocular contents
- While there is no definitive evidence on the most effective pre-emptive treatment, intravitreal ceftazidime plus vancomycin may reduce infection rate in high-risk cases if they can be safely administered at the time of surgery
- Moxifloxacin has better intraocular penetration than ciprofloxacin; however, ciprofloxacin can be used if moxifloxacin is not available
- Moxifloxacin is not licensed for use in children on the basis of animal studies that showed an adverse effect on cartilage development with quinolone use; however, there are few data from human trials to support this finding. Moxifloxacin can be used in children when it is the drug of choice
- Ciprofloxacin is not licensed for use in children on the basis of animal studies that showed an adverse effect on cartilage development with quinolone use; however, there are few data from human trials to support this finding. Ciprofloxacin can be used in children when it is the drug of choice
References:
See section on penetrating eye injuries - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Scabies grading calculator
Scabies Grading Table
| Scabies Score |
Grade |
| 4-6 |
Grade 1 |
| 7-9 |
Grade 2 |
| 10-12 |
Grade 3 |
Grade 1 scabies treatment
For grade 1 scabies:
Ivermectin 200 mcg/kg rounded up to the nearest 1.5 mg orally, for three
doses on days 0,1 and 7.
AND either
① Benzyl benzoate with added tea tree
oil at 5% concentration (available from pharmacy) second daily for first week, and twice
weekly thereafter until cured
OR
① Permethrin 5% second daily for the
first week, then twice weekly thereafter until cured
AND with either of the above topical agents, on non treatment days, to the
crusted areas apply:
② Calmurid® (urea 10%, lactic
acid 5%) second daily until hyperkeratosis has resolved.
Code for ivermectin is:
1sca
This code is valid for ONE day only. Starting from the
first day of treatment for this condition. Infectious diseases must be contacted within 24 hours for
all crusted scabies patients. Please annotate this code on the medication chart and document when
infectious diseases are to be contacted in the patient notes.
- Take skin scrapings around day 5 for grade 1 crusted scabies to ensure treatment is successful
- Ensure topical agents are applied after the patient normally bathes or showers for the day
- For each admission take skin scrapings, FBC, CRP, LFTs, U+E, blood cultures and pregnancy test for
females prior to ivermectin
- Ensure ivermectin is taken with a high fat meal to ensure absorption
- It is important to ensure that the dosage of ivermectin is rounded to the nearest 1.5 mg to ensure
that half tablets can be given
- Patients with crusted scabies should remain in isolation until approved for clearance by infection
control and infectious diseases
- The non-Government organisation ‘One Disease’ is tackling the issue of Crusted Scabies in the Top
End. They can assist with education and follow-up of patients and education/treatment of household
contacts. They should be notified of all cases of confirmed crusted scabies
- Antibiotics may be required for secondary bacterial sepsis, which may not be clinically evident and
may involve multiple organisms, including Gram-negatives in addition to S. aureus and S. pyogenes.
Please contact infectious diseases if sepsis or secondary infection is suspected
- Environmental Measures
- For patient: hospitalisation preferable, with single room isolation and contact precautions
whilst caring for patient (long-sleeved gown, gloves, shoes and hair cover). Bin for PPE should
be placed inside the room, so PPE can be removed and binned prior to exit
- The nail beds can serve as a reservoir for mites. Trim nails adequately, and if concerned about
concurrent tinea infection of nails, send clippings for fungal microscopy and culture and
consider treatment with oral terbinafine
- Treat all household members with topical therapy (see Scabies guidelines in eTG and CARPA)
- Wash bed linen and clothes in hot water (50-60°c)
- Consider insecticide bombing or fumigation (by EHO) of each room of the house
- Vacuum cleaning can be used to suck up mites
- Decontaminate items that cannot be washed by removing from any contact for at least 3 days,
allowing the scabies mites to die
References:
See section on crusted scabies - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Grade 2 scabies treatment
For grade 2 scabies:
Ivermectin 200 mcg/kg rounded up to the nearest 1.5 mg orally for five
doses on days 0,1,7,8 and 14.
AND either
① Benzyl benzoate with added tea tree
oil at 5% concentration and twice weekly thereafter until cured
OR
① Permethrin 5% second daily for the
first week, then twice weekly thereafter until cured
AND with either of the above topical agents, on non treatment days, to the
crusted areas apply:
② Calmurid® (urea 10%, lactic acid
5%) second daily until hyperkeratosis has resolved.
Code for ivermectin is:
1sca
This code is valid for ONE day only. Starting from the
first day of treatment for this condition. Infectious diseases must be contacted within 24 hours for
all crusted scabies patients. Please annotate this code on the medication chart and document when
infectious diseases are to be contacted in the patient notes.
- Grade 2 scabies usually need to be isolated until at least 7 days of treatment, but a scraping could
be sent at day 6 to confirm treatment is successful and skin clear in preparation for de-isolation
- Ensure topical agents are applied after the patient normally bathes or showers for the day
- For each admission take skin scrapings, FBC, CRP, LFTs, U+E, blood cultures and pregnancy test for
females prior to ivermectin
- Ensure ivermectin is taken with a high fat meal to ensure absorption
- It is important to ensure that the dosage of ivermectin is rounded to the nearest 1.5 mg to ensure
that half tablets can be given
- Patients with crusted scabies should remain in isolation until approved for clearance by infection
control and infectious diseases
- The non-Government organisation ‘One Disease’ is tackling the issue of Crusted Scabies in the Top
End. They can assist with education and follow-up of patients and education/treatment of household
contacts. They should be notified of all cases of confirmed crusted scabies
- Antibiotics may be required for secondary bacterial sepsis, which may not be clinically evident and
may involve multiple organisms, including Gram-negatives in addition to S. aureus and S. pyogenes.
Please contact infectious diseases if sepsis or secondary infection is suspected
- Environmental Measures
- For patient: hospitalisation preferable, with single room isolation and contact precautions
whilst caring for patient (long-sleeved gown, gloves, shoes and hair cover). Bin for PPE should
be placed inside the room, so PPE can be removed and binned prior to exit
- The nail beds can serve as a reservoir for mites. Trim nails adequately, and if concerned about
concurrent tinea infection of nails, send clippings for fungal microscopy and culture and
consider treatment with oral terbinafine
- Treat all household members with topical therapy (see Scabies guidelines in eTG and CARPA)
- Wash bed linen and clothes in hot water (50-60°c)
- Consider insecticide bombing or fumigation (by EHO) of each room of the house
- Vacuum cleaning can be used to suck up mites
- Decontaminate items that cannot be washed by removing from any contact for at least 3 days,
allowing the scabies mites to die
References:
See section on crusted scabies - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Grade 3 scabies treatment
For grade 3 scabies:
Ivermectin 200 mcg/kg rounded up to the nearest 1.5 mg orally for seven doses
on days 0,1,7,8,14,21 and 28.
AND either
① Benzyl benzoate with added tea tree
oil at 5% concentration (available from pharmacy) second daily for first week, and twice weekly
thereafter until cured
OR
① Permethrin 5% second daily for the
first week, then twice weekly thereafter until cured
AND with either of the above topical agents, on non treatment days, to the
crusted areas apply:
② Calmurid® (urea 10%, lactic acid
5%) second daily until hyperkeratosis has resolved.
Code for ivermectin is:
1sca
This code is valid for ONE day only. Starting from the
first day of treatment for this condition. Infectious diseases must be contacted within 24 hours for
all crusted scabies patients. Please annotate this code on the medication chart and document when
infectious diseases are to be contacted in the patient notes.
- Grade 3 crusted scabies usually require isolation for 10-14 days at least, however a repeat scraping
at day 7 is recommended to assess mite load. If this remains positive check topical treatment is
being adequately applied and ivermectin dosing is correct
- Ensure topical agents are applied after the patient normally bathes or showers for the day
- For each admission take skin scrapings, FBC, CRP, LFTs, U+E, blood cultures and pregnancy test for
females prior to ivermectin
- Ensure ivermectin is taken with a high fat meal to ensure absorption
- It is important to ensure that the dosage of ivermectin is rounded to the nearest 1.5 mg to ensure
that half tablets can be given
- Patients with crusted scabies should remain in isolation until approved for clearance by infection
control and infectious diseases
- The non-Government organisation ‘One Disease’ is tackling the issue of Crusted Scabies in the Top
End. They can assist with education and follow-up of patients and education/treatment of household
contacts. They should be notified of all cases of confirmed crusted scabies
- Antibiotics may be required for secondary bacterial sepsis, which may not be clinically evident and
may involve multiple organisms, including Gram-negatives in addition to S. aureus and S. pyogenes.
Please contact infectious diseases if sepsis or secondary infection is suspected
- Environmental Measures
- For patient: hospitalisation preferable, with single room isolation and contact precautions
whilst caring for patient (long-sleeved gown, gloves, shoes and hair cover). Bin for PPE should
be placed inside the room, so PPE can be removed and binned prior to exit
- The nail beds can serve as a reservoir for mites. Trim nails adequately, and if concerned about
concurrent tinea infection of nails, send clippings for fungal microscopy and culture and
consider treatment with oral terbinafine
- Treat all household members with topical therapy (see Scabies guidelines in eTG and CARPA)
- Wash bed linen and clothes in hot water (50-60°c)
- Consider insecticide bombing or fumigation (by EHO) of each room of the house
- Vacuum cleaning can be used to suck up mites
- Decontaminate items that cannot be washed by removing from any contact for at least 3 days,
allowing the scabies mites to die
References:
See section on crusted scabies - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Shingles
How long has it been since rash onset?
Shingles
Is the patient immunocompromised?
Shingles
Is the patient immunocompromised?
Shingles
Is there widespread/disseminated disease?
- Widespread disease is characterised by rash in > 1 dermatome often accompanied by systemic
symptoms
Shingles treatment
If patient is immunocompromised and has disseminated shingles:
Aciclovir 10 mg/kg IV, 8-hourly for adults
OR if patient is a child
Aciclovir 500 mg/m2 IV, 8-hourly. (approximately 20mg/kg
for a child 5 years or younger, 15mg/kg for a child over 5 years of age)
Code for aciclovir iv is:
3shi
This code is valid for THREE days only, starting from the
first day of treatment for this condition. Infectious diseases must be contacted if IV treatment is
to continue past 72 hours. Please annotate this code on the medication chart and document when
infectious diseases are to be contacted in the patient notes.
- Treatment should continue for 10-14 days (IV + PO)
- If ocular involvement is present or suspected please contact ophthalmology promptly for review. This
includes involvement of the first division of the trigeminal nerve, particularly if there are
lesions on the nose as they signify involvement of the nasociliary branch which also innervates the
globe
- Treat acute neuropathic pain associated with shingles as per recommendations in the Therapeutic Guidelines section on neuropathic pain
- For patients over 60 years of age a vaccine is available and may be indicated despite previous
herpes zoster infection. See the Australian Immunisation Handbook on the library database for
details
- In herpes zoster, transmission occurs with both contact and aerosolisation of the vesicle fluid.
Airborne Transmission Based precautions must be used when caring for the patient
- After significant clinical improvement switch to oral antiviral therapy (see regimen for uncomplicated shingles) to complete 7 days total (IV + oral)
- To calculate body surface area in paediatrics use:
√ (Height (cm) x Weight (kg)) ÷ 3600
References:
See section on herpes zoster therapy - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Shingles treatment
Uncomplicated shingles treatment:
① Valaciclovir 1 g orally, 8-hourly for
7 days
OR
① Famclovir 500 mg orally, 8-hourly for
7 days or 10-days for patients who are immunocompromised
OR
② Aciclovir 800 mg orally, five times
daily for 7 days
OR if patient is a child
② Aciclovir 20 mg/kg up to 800 mg
orally, five times daily for 7 days
Code for PO aciclovir or PO valaciclovir is:
7shi
This code is valid for SEVEN days only, starting from the
first day of treatment for this condition. Infectious diseases must be contacted if treatment is to
continue past one week. Please annotate this code on the medication chart and document when
infectious diseases are to be contacted in the patient notes.
- If ocular involvement is present or suspected please contact ophthalmology promptly for review. This
includes involvement of the first division of the trigeminal nerve, particularly if there are
lesions on the nose as they signify involvement of the nasociliary branch which also innervates the
globe
- There is evidence that oral valaciclovir is more effective than oral aciclovir in reducing pain in
patients with shingles
- Treat acute neuropathic pain associated with shingles as per recommendations in the Therapeutic Guidelines section on neuropathic pain
- There is more safety data to support the use of aciclovir in pregnancy, however there is also some
evidence that valaciclovir is safe in pregnancy
- For patients over 60 years of age a vaccine is available and may be indicated despite previous
herpes zoster infection. See the Australian Immunisation Handbook on the library database for
details
- In herpes zoster, transmission occurs with both contact and aerosolisation of the vesicle fluid.
Airborne Transmission Based precautions must be used when caring for the patient
References:
See section on herpes zoster therapy - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Shingles treatment
Uncomplicated shingles treatment:
In a non-immunocompromised patient there is little benefit from antiviral
therapy if the onset of the rash was more than 72 hours prior to presentation.
- There may be some circumstances where treatment may be indicated please contact the infectious
diseases team to discuss particular concerns
- If ocular involvement is present or suspected please contact ophthalmology promptly for review. This
includes involvement of the first division of the trigeminal nerve, particularly if there are
lesions on the nose as they signify involvement of the nasociliary branch which also innervates the
globe
- Treat acute neuropathic pain associated with shingles as per recommendations in the Therapeutic
Guidelines section on neuropathic pain
- In herpes zoster, transmission occurs with both contact and aerosolisation of the vesicle fluid.
Airborne Transmission Based precautions must be used when caring for the patient
- For patients over 60 years of age a vaccine is available and may be indicated despite previous
herpes zoster infection. See the Australian Immunisation Handbook on the library database for
details
References:
See section on herpes zoster therapy - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Is surgical prophylaxis required?
- Common procedures which do not routinely require surgical prophylaxis are:
- Clean breast surgery without implantation or removal of malignancy
- Lymph node biopsy
- Hernia repair without insertion of prosthetic material (in patient with BMI < 30)
- Surgery on varicose veins without the insertion of prosthetic material
- Superficial surgery through clean skin (clean plastic surgery)
- Routine upper or lower gastroinstestinal endoscopy
- Myringoplasty or tympanoplasty
- Routine arthroscopy
- If the patient is already on antibiotics, surgical prophylaxis is not required if:
- The antimicrobial matches the surgical prophylaxis regimen
- Less than two half lives passed since the antibiotic was last administered (see antibiotic half lives table)
- And surgery is expected to finish within 2 half lives of the antibiotic (see antibiotic half lives table)
What type of surgery is being performed?
- The critical period for successful prophylaxis is 4 hours following implantation of organisms into a
wound
- In general, a single preoperative dose of a parenteral drug is sufficient and should be given within
30 min preceding the first skin incision
- If the operation is delayed, if there is significant blood loss during surgery, or if surgery is
prolonged then a second dose may be required. See the table below for details
Surgical prophylaxis
Is the patient known to be, or at risk of colonisation with MRSA?
(See below)
Risk factors for MRSA colonisation are:
- Risk factors for MRSA infection include: residence in a jail or detention centre, indigenous
heritage, previous MRSA colonisation which has not been cleared, hospital stay for > 5 days
immediately prior to surgery
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Surgical prophylaxis
Is gentamicin contraindicated in this patient?
(See below)
Aminoglycoside Contraindications and Precautions
| Contraindications |
Precautions |
| History of vestibular or auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
Pre-existing significant auditory impairment (hearing loss or tinnitus) |
| History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to an aminoglycoside (rare) |
Pre-existing vestibular condition (dizziness, vertigo or balance problems) |
| Myasthenia gravis |
Family history (first-degree relative) of auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
- A single dose can be used in patients with:
- Chronic renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min) or rapidly deteriorating
renal function
- Advanced age (eg 80 years or older), depending on calculated renal function
- If you are unsure whether gentamicin is appropriate for this patient please consult infectious
diseases
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient with life-threatening penicillin
reaction/anaphylaxis use:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Trimethoprim+sulfamethoxazole 160+800 mg (child 1 month or older:
4+20 mg/kg up to 160+800 mg) orally, within 30 minutes before surgical incision.
AND
Metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within
120 minutes before surgical incision, then consider repeating the dose after 12 hours
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient with life-threatening penicillin
reaction/anaphylaxis use:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Trimethoprim+sulfamethoxazole 160+800 mg (child 1 month or older:
4+20 mg/kg up to 160+800 mg) orally, within 30 minutes before surgical incision.
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Amputation of lower limb treatment
For surgical prophylaxis prior to amputation of an ischaemic lower limb in a
patient with life-threatening penicillin reaction/anaphylaxis use:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Gentamicin (adult and child) 5 mg/kg IV, within 30 minutes before
surgical incision.
AND
Metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within
120 minutes before surgical incision, then consider repeating the dose after 12 hours
- If actual body weight is more than 20% over the ideal body weight, use ideal body weight to
calculate the dose. For morbidly obese patients, seek expert advice
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Amputation of lower limb treatment
For surgical prophylaxis prior to amputation of a non-ischaemic lower limb
in a patient with life-threatening penicillin reaction/anaphylaxis or cephalosporin allergy:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Gentamicin (adult and child) 5 mg/kg IV, within 30 minutes before
surgical incision.
- If actual body weight is more than 20% over the ideal body weight, use ideal body weight to
calculate the gentamicin dose. For morbidly obese patients, seek expert advice
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Amputation of lower limb treatment
For surgical prophylaxis prior to amputation of a lower limb in a patient
without life-threatening penicillin reaction/anaphylaxis or cephalosporin allergy, at risk of MRSA
use:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Cefazolin 2 g (child or adult < 40kg: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV,
within 60 minutes before surgical incision, and if the operation is prolonged a second dose
should be given after 3 hours. Postoperatively continue 8-hourly for up to 2 further
doses.
AND
Metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within
120 minutes before surgical incision, then consider repeating the dose after 12 hours
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient without life-threatening penicillin
reaction/anaphylaxis use:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Cefazolin 2 g (child or adult < 40kg: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV,
within 60 minutes before surgical incision, then 8-hourly for up to 2 further doses.
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Amputation of lower limb treatment
For surgical prophylaxis prior to amputation of a lower limb in a patient
without a life threatening reaction/anaphylaxis to penicillin at low risk of MRSA use:
Cefazolin 2 g (child or adult < 40kg: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV,
within 60 minutes before surgical incision, then 8-hourly for up to 2 further doses.
AND
Metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within
120 minutes before surgical incision, then consider repeating the dose after 12 hours.
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some
cardiac and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb
amputation). Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical
procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups.
Therapeutic guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Amputation of lower limb treatment
For surgical prophylaxis prior to amputation of a lower limb in a patient
without a life threatening reaction/anaphylaxis to penicillin at low risk of MRSA:
Cefazolin 2 g (child or adult < 40kg: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV,
within 60 minutes before surgical incision, then 8-hourly for up to 2 further doses.
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some
cardiac and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb
amputation). Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical
procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups.
Therapeutic guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical Prophylaxis not Recommended
Surgical prophylaxis is not normally recommended for this procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Vascular surgery
Is the patient known to be, or at risk of colonisation with MRSA?
(See below)
Risk factors for MRSA colonisation are:
- Risk factors for MRSA infection include: residence in a jail or detention centre, indigenous
heritage, previous MRSA colonisation which has not been cleared, hospital stay for > 5 days
immediately prior to surgery
Vascular surgery
Is the patient known to be, or at risk of colonisation with MRSA?
(See below)
Risk factors for MRSA colonisation are:
- Risk factors for MRSA infection include: residence in a jail or detention centre, indigenous
heritage, previous MRSA colonisation which has not been cleared, hospital stay for > 5 days
immediately prior to surgery
Surgical prophylaxis
Is gentamicin contraindicated in this patient?
(See below for contraindications)
Aminoglycoside Contraindications and Precautions
| Contraindications |
Precautions |
| History of vestibular or auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
Pre-existing significant auditory impairment (hearing loss or tinnitus) |
| History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to an aminoglycoside (rare) |
Pre-existing vestibular condition (dizziness, vertigo or balance problems) |
| Myasthenia gravis |
Family history (first-degree relative) of auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
- A single dose can be used in patients with:
- Chronic renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min) or rapidly deteriorating
renal function
- Advanced age (eg 80 years or older), depending on calculated renal function
- If you are unsure whether gentamicin is appropriate for this patient please consult infectious
diseases
Surgical prophylaxis
Is gentamicin contraindicated in this patient?
(See below for contraindications)
Aminoglycoside Contraindications and Precautions
| Contraindications |
Precautions |
| History of vestibular or auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
Pre-existing significant auditory impairment (hearing loss or tinnitus) |
| History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to an aminoglycoside (rare) |
Pre-existing vestibular condition (dizziness, vertigo or balance problems) |
| Myasthenia gravis |
Family history (first-degree relative) of auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
- A single dose can be used in patients with:
- Chronic renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min) or rapidly deteriorating
renal function
- Advanced age (eg 80 years or older), depending on calculated renal function
- If you are unsure whether gentamicin is appropriate for this patient please consult infectious
diseases
Surgical prophylaxis
For surgery in a patient with a life threatening reaction/anaphylaxis to
penicillin without MRSA risk factors use:
Gentamicin (adult and child) 2 mg/kg IV, within 120 minutes
before surgical incision
AND
Metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within
120 minutes before surgical incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
For surgery in a patient with a life threatening reaction/anaphylaxis to
penicillin without MRSA risk factors use:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Gentamicin (adult and child) 2 mg/kg IV, within 120 minutes
before surgical incision
AND
Metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within
120 minutes before surgical incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
For surgery in a patient with a life threatening reaction/anaphylaxis to
penicillin, intolerant of gentamicin use:
Metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within
120 minutes before surgical incision
AND
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
- Please check the patients previous microbiology. If past MRSA is sensitive to
trimethoprim+sulfamethoxazole then this will be sufficient for prophylaxis, if it was resistant then
please add teicoplanin as per treatment for an MRSA colonised patient without
gentamicin contraindications
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
For surgery in a patient with a life threatening reaction/anaphylaxis to
penicillin, intolerant of gentamicin use:
Metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within
120 minutes before surgical incision
AND
Trimethoprim+sulfamethoxazole 160+800 mg (child 1 month or older:
5+25 mg/kg up to 160+800 mg) IV, within 30 minutes before surgical incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis recommendation
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient in a patient without life-threatening
penicillin reaction/anaphylaxis use:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Cefazolin 2 g (child or adult < 40kg: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV,
within 60 minutes before surgical incision
AND
Metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within
120 minutes before surgical incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis recommendation
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient in a patient without life-threatening
penicillin reaction/anaphylaxis use:
Cefazolin 2 g (child or adult < 40kg: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV,
within 60 minutes before surgical incision
AND
Metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within
120 minutes before surgical incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Is antibiotic prophylaxis confirmed as necessary?
Surgical prophylaxis not indicated:
- laparoscopic surgery in the absence of risk fators for postoperative infection (see
below)
|
Surgical prophylaxis indicated:
- laparoscopic surgery ONLY if patient has risk factors for postoperative infection
- age >70 years
- diabetes
- obstructive jaundice
- common bile duct stones
- acute cholecystitis
- non-functioning gallbladder
- Open cholecystectomy
|
Surgical prophylaxis may not be required:
|
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Oral Maxillofacial Surgical prophylaxis
Is antibiotic prophylaxis confirmed as necessary?
Surgical prophylaxis not indicated:
- clean or clean–contaminated procedures
- procedures involving insertion of dental implants
|
Surgical prophylaxis indicated:
- procedures involving insertion of prosthetic material, with the exception of dental
implants
- open reduction and internal fixation of mandibular fractures or midfacial (eg Le
Fort or zygomatic) fractures
- intraoral bone grafting procedures
- orthognathic surgery (major jaw realignment surgery)
- cleft lip and palate repairs
|
Specific patient considerations:
- patients a procedure that involves manipulation of the gingival or periapical tissue
or perforation of the oral mucosa, prophylaxis against streptococcal endocarditis is
required (refer to “endocarditis prophylaxis in dental procedures” in therapeutic
guidelines)
|
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Is antibiotic prophylaxis confirmed as necessary?
Surgical prophylaxis not indicated:
- nasal packing or a tamponade device in situ following epistaxis
- uncomplicated nose or sinus surgery (including endoscopic procedures)
- uncomplicated ear surgery
- otoplasty
- stapedectomy
- tonsillectomy [see specific patient considerations]
- adenoidectomy [see specific patient considerations]
|
Surgical prophylaxis indicated:
- major ear surgery
- complex septorhinoplasty
- revision sinus surgery
- laryngectomy (primary or salvage)
- tympanomastoid surgery
- hearing implant procedures, including cochlear implant procedures
|
Specific patient considerations:
- patients undergoing tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy with specific cardiac conditions
(refer to “prevention of infective endocarditis” in Therapeutic Guidelines)
|
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Is antibiotic prophylaxis confirmed as necessary?
Surgical prophylaxis not indicated:
- cerebrospinal fluid leakage following
- vaccinate against Streptococcus pneumoniae to protect against the
development of pneumococcal meningitis. See the Australian Immunisation
Handbook
|
Surgical prophylaxis indicated:
- intracranial shunt insertion
- pressure monitor insertion
- craniotomy
- microsurgery
- procedures involving insertion of prosthetic material
- re-exploration procedures
- external ventricular drain insertion
|
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Is antibiotic prophylaxis confirmed as necessary?
Surgical prophylaxis not indicated:
- varicose veins procedures
- brachial or carotid artery procedures, unless prosthetic material is inserted
|
Surgical prophylaxis indicated:
- limb amputation
- vascular reconstructive surgery involving abdominal aorta or lower limbs and limb
amputation surgery
|
Surgical prophylaxis may not be required:
- patient already receiving antibiotic treatment for an established infection with
activity against the organism(s) most likely to cause postoperative infection (this
should include anaerobic cover for ischaemic limb amputation). (see antibiotic half lives table)
- Adjust timing of antibiotics prior to surgery
- Intra-operative re-dosing may be required
|
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Is prophylaxis for amputation of a limb?
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Is antibiotic prophylaxis confirmed as necessary?
Surgical prophylaxis not indicated:
- diagnostic excisional biopsy
- stand-alone sentinel node biopsy
- lumpectomy (with or without needle or wire localisation)
|
Surgical prophylaxis indicated:
- reduction mammoplasty
- simple mastectomy
- wide local excision
- axillary lymph node clearance
- nipple surgery
- all repeat or revision procedures
- prosthetic breast reconstruction surgery (prosthetic implant or acellular dermal
matrix)
- autologous breast reconstruction surgery
- breast augmentation surgery
|
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Is antibiotic prophylaxis confirmed as necessary?
Surgical prophylaxis not indicated:
- laparoscopic procedures that do not enter the bowel or vagina
- hysteroscopy, operative or diagnostic
- dilation and curettage, with the exception of surgical termination of pregnancy
- endometrial biopsy or ablation
- insertion of an intrauterine device
- cervical tissue excision procedure (eg LLETZ, biopsy, endocervical curettage)
- autologous mid-urethral sling procedures
|
Surgical prophylaxis indicated:
- Hysterectomy
- gynaecological–oncological procedures
- gynaecological laparotomy procedures
- synthetic mid-urethral sling procedures
- pelvic organ prolapse procedures
- surgical termination of pregnancy if not investigated for STIs before the procedure
|
Specific patient considerations:
- Patients with specific cardiac conditions may require additional antibiotics for
prophylaxis against enterococcal endocarditis (refer to “endocarditis prophylaxis
for gastrourinary and gastrointestinal
|
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Surgical prophylaxis
Will the procedure involve incision through the oral mucosa only?
(e.g. cleft lip or palate repair)
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Surgical prophylaxis
Is the patient known to be, or at risk of colonisation with MRSA?
(See below)
Risk factors for MRSA colonisation are:
- Risk factors for MRSA infection include: residence in a jail or detention centre, indigenous
heritage, previous MRSA colonisation which has not been cleared, hospital stay for > 5 days
immediately prior to surgery
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Is the patient known to be, or at risk of colonisation with MRSA?
(See below)
Risk factors for MRSA colonisation are:
- Risk factors for MRSA infection include: residence in a jail or detention centre, indigenous
heritage, previous MRSA colonisation which has not been cleared, hospital stay for > 5 days
immediately prior to surgery
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient at risk of MRSA, without
life-threatening penicillin reaction/anaphylaxis use:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Cefazolin 2 g (child or adult < 40kg: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV,
within 60 minutes before surgical incision.
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Does the patient have a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to
penicillin or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Surgical prophylaxis
Is gentamicin contraindicated in this patient?
(See below)
Aminoglycoside Contraindications and Precautions
| Contraindications |
Precautions |
| History of vestibular or auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
Pre-existing significant auditory impairment (hearing loss or tinnitus) |
| History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to an aminoglycoside (rare) |
Pre-existing vestibular condition (dizziness, vertigo or balance problems) |
| Myasthenia gravis |
Family history (first-degree relative) of auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
- A single dose can be used in patients with:
- Chronic renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min) or rapidly deteriorating
renal function
- Advanced age (eg 80 years or older), depending on calculated renal function
- If you are unsure whether gentamicin is appropriate for this patient please consult infectious
diseases
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient with life-threatening penicillin
reaction/anaphylaxis use:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Trimethoprim+sulfamethoxazole 160+800 mg (child 1 month or older:
5+25 mg/kg up to 160+800 mg) IV, within 30 minutes before surgical incision.
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient with life-threatening penicillin
reaction/anaphylaxis use:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Gentamicin (adult and child) 2 mg/kg IV, within 120 minutes
before surgical incision.
- If actual body weight is 20% or more above ideal body weight dose gentamicin based on ideal body
weight
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient without life-threatening penicillin
reaction/anaphylaxis or cephalosporin allergy:
Cefazolin 2 g (child or adult <40kg: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV,
within 60 minutes before surgical incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Is surgical prophylaxis required?
- Common head and neck procedures which do not routinely require surgical prophylaxis are:
- Thyroidectomy
- simple lymph node excision (including submandibular lymph node excision)
- parotidectomy
- clean procedures (not listed above)
- If the patient is already on antibiotics, surgical prophylaxis is not required if:
- The antimicrobial matches the surgical prophylaxis regimen
- Less than two half lives passed since the antibiotic was last administered (see antibiotic half lives table)
- And surgery is expected to finish within 2 half lives of the antibiotic (see antibiotic half lives table)
Will the incision be through mucosal surfaces?
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Head, neck or hysterectomy prophylaxis
For a patient with life-threatening penicillin reaction/anaphylaxis
use:
Clindamycin 600 mg (child:15 mg/kg up to 600 mg) IV, within 120
minutes before surgical incision
PLUS for extensive neck dissection, or debulking or reconstructive surgery
Gentamicin 2 mg/kg IV, over 3-5 minutes, within 120 minuted before
surgical incision
- When gentamicin is indicated, if there is at least a moderate likelihood that the procedure will
continue longer than 6 hours then consider using a 5mg/kg dose
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Head, neck or hysterectomy prophylaxis
For a patient with life-threatening penicillin reaction/anaphylaxis
use:
Clindamycin 600 mg (child:15 mg/kg up to 600 mg) IV, within 120
minutes before surgical incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Is surgery predicted to be complicated?
(i.e. Is entry into the bowel lumen anticipated?)
Surgical prophylaxis
Is the hysterectomy abdominal or vaginal?
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
Diagnostic Criteria for Penicillin Allergy:
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Surgical prophylaxis
Is the procedure a re-operation of a joint arthroplasty?
Surgical prophylaxis
Is the procedure a re-operation of a joint arthroplasty?
Surgical prophylaxis
Is the patient known to be, or at risk of colonisation with MRSA?
(See below)
Risk factors for MRSA colonisation are:
- Risk factors for MRSA infection include: residence in a jail or detention centre, indigenous
heritage, previous MRSA colonisation which has not been cleared, hospital stay for > 5 days
immediately prior to surgery
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Major joint arthroplasty prophylaxis
For major orthopaedic surgery in a patient with a life threatening
reaction/anaphylaxis to penicillin use:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Minor elective orthopaedic surgery prophylaxis
For orthopaedic surgery in a patient with a life threatening
reaction/anaphylaxis to penicillin use as a single dose:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis for termination of pregnancy give:
Azithromycin 1 g PO, 2-3 hours prior to the procedure
AND
Metronidazole 1 g suppository PR, at the time of the procedure
- The Therapeutic Guidelines recommend doxycycline 4g po prior to termination of pregnancy however due
to poor tolerability a single dose of azithromycin and PR metronidazole is the preferred regimen for
TEHS patients (as per the RCOG guidelines)
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Is there any obstruction present?
- Obstruction could be due to postoperative adhesions, malignancy, Crohn disease or hernia
Surgical prophylaxis
Is antibiotic prophylaxis confirmed as necessary?
Surgical prophylaxis not indicated:
- urodynamic studies
- extracorporeal shock-wave lithotripsy
- open or laparoscopic urological procedures in which the urinary tract is not entered
(eg vasectomy, scrotal surgery, varicocele ligation) and prosthetic material is not
implanted
|
Surgical prophylaxis indicated:
- prostate fiducial marker insertion
- endoscopic intrarenal and ureteric stone procedures (e.g. percutaneous
nephrolithotomy, pyeloscopy for ureteric or kidney stones)
- ureteroscopy procedures
- Other endoscopic or uncomplicated cytoscopic diagnostic procedures ONLY If there are
risks for postoperative infection (e.g. urinary tract obstruction or abnormalities,
urinary stones, indwelling or externalised catheters)
- transurethral resection of the prostate
- transrectal prostate biopsy
- transperineal prostate biopsy
- open or laparoscopic urological procedures involving implantation of prosthetic
material (eg penile prostheses, artificial urinary sphincters, mesh)
- ureteroscopy procedures
- open or laparoscopic urological procedures where the urinary tract is entered
|
Individual patient based decision:
- specific risks for postoperative infection (e.g. lithotripsy in patients with an
internal stent, nephrostomy tube or indwelling catheter in situ)
- immediate operation and bacteriuria cannot be excluded
|
- Antibiotic prophylaxis is not recommended for non-invasive urological surgery in a patient with
sterile urine
- For:
- Endoscopic urological procedures:
- Propylaxis is not required for non–invasive urological surgery (eg diagnostic
cystoscopy) in a patient with sterile urine. Antibiotic prophylaxis is indicated
if there are specific risk factors for infection (renal and ureteric stone
procedures, tumor resection, ureteric obstruction)
- Open or laparoscopic urological procedures:
- Prophylaxis is not required for open or laparoscopic urological procedures where the
urinary tract is not entered (eg vasectomy, scrotal surgery, varicocele
ligation) in a patient with sterile urine, unless there are specific risk
factors for infection (eg urinary tract obstriction), or the procedure
involves prosthetic material
- TURP and Transrectal prostatic biopsy:
- Prophylaxis is always required
- Preoperative treatment of bacteriuria does not negate the need for surgical antibiotic prophylaxis.
An exception is when gentamicin is given preoperatively to treat bacteriuria and is also indicated
as prophylaxis
Urological surgery
What type of procedure is being performed?
Urological surgery
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Urological surgery
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Urological surgery
Is gentamicin contraindicated in this patient?
(See below)
Aminoglycoside Contraindications and Precautions
| Contraindications |
Precautions |
| History of vestibular or auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
Pre-existing significant auditory impairment (hearing loss or tinnitus) |
| History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to an aminoglycoside (rare) |
Pre-existing vestibular condition (dizziness, vertigo or balance problems) |
| Myasthenia gravis |
Family history (first-degree relative) of auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
- A single dose can be used in patients with:
- Chronic renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min) or rapidly deteriorating
renal function
- Advanced age (eg 80 years or older), depending on calculated renal function
- If you are unsure whether gentamicin is appropriate for this patient please consult infectious
diseases
Urological surgery
Is gentamicin contraindicated in this patient?
(See below)
Aminoglycoside Contraindications and Precautions
| Contraindications |
Precautions |
| History of vestibular or auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
Pre-existing significant auditory impairment (hearing loss or tinnitus) |
| History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to an aminoglycoside (rare) |
Pre-existing vestibular condition (dizziness, vertigo or balance problems) |
| Myasthenia gravis |
Family history (first-degree relative) of auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
- A single dose can be used in patients with:
- Chronic renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min) or rapidly deteriorating
renal function
- Advanced age (eg 80 years or older), depending on calculated renal function
- If you are unsure whether gentamicin is appropriate for this patient please consult infectious
diseases
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis use:
Gentamicin (adult and child) 2 mg/kg IV, within 120 minutes
before surgical incision.
AND either
① Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120
minutes before surgical incision (recommended rate 10 mg/min)
OR
① Clindamycin 600mg IV, started within
the 120 minutes before the procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
- If there is untreated bacteruria the gentamicin dose should be increased to 3mg/kg
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
Surgical prophylaxis is not normally recommended
Surgical prophylaxis is not normally required. Please contact
infectious diseases if patient has risk factors which may warrant surgical prophylaxis
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis use:
Gentamicin (adult and child) 2 mg/kg IV, within 120 minutes
before surgical incision.
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
- If there is untreated bacteruria the gentamicin dose should be increased to 3mg/kg
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Urological surgery
Is gentamicin contraindicated in this patient?
(See below)
Aminoglycoside Contraindications and Precautions
| Contraindications |
Precautions |
| History of vestibular or auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
Pre-existing significant auditory impairment (hearing loss or tinnitus) |
| History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to an aminoglycoside (rare) |
Pre-existing vestibular condition (dizziness, vertigo or balance problems) |
| Myasthenia gravis |
Family history (first-degree relative) of auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
- A single dose can be used in patients with:
- Chronic renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min) or rapidly deteriorating
renal function
- Advanced age (eg 80 years or older), depending on calculated renal function
- If you are unsure whether gentamicin is appropriate for this patient please consult infectious
diseases
Urological surgery
Is gentamicin contraindicated in this patient?
(See below)
Aminoglycoside Contraindications and Precautions
| Contraindications |
Precautions |
| History of vestibular or auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
Pre-existing significant auditory impairment (hearing loss or tinnitus) |
| History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to an aminoglycoside (rare) |
Pre-existing vestibular condition (dizziness, vertigo or balance problems) |
| Myasthenia gravis |
Family history (first-degree relative) of auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
- A single dose can be used in patients with:
- Chronic renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min) or rapidly deteriorating
renal function
- Advanced age (eg 80 years or older), depending on calculated renal function
- If you are unsure whether gentamicin is appropriate for this patient please consult infectious
diseases
Urological surgery
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to
penicillin?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient with a life threatening
reaction/anaphylaxis to penicillin intolerant of gentamicin use:
Trimethoprim+sulfamethoxazole 160+800 mg (child 1 month or older:
4+20 mg/kg up to 160+800 mg) orally, within 30 minutes before surgical incision.
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient with life-threatening penicillin
reaction/anaphylaxis use:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Gentamicin (adult and child) 2 mg/kg IV, within 120 minutes
before surgical incision.
- If actual body weight is 20% or more above ideal body weight dose gentamicin based on ideal body
weight
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
- If patient has untreated bacteruria increase the gentamicin dose to 3mg/kg
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis for transrectal prostatic biopsy in a patient with
no recent travel to SE Asia use:
Ciprofloxacin 500 mg orally, as a single dose, 60 to 120 minutes before
the procedure.
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
Code for ciprofloxacin is:
1uro
This code is valid for A SINGLE DOSE only. IFD must be
contacted if any further doses are to be given
If the procedure is delayed beyond 6 hours the 500 mg dose should be repeated prior to
surgery
If the patient has had recent travel to South East Asia contact infectious diseases as
they may be colonised with an ESBL producing organism
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Urological surgery
Is entry into the bowel lumen anticipated?
Urological surgery
Is gentamicin contraindicated in this patient?
(See below)
Aminoglycoside Contraindications and Precautions
| Contraindications |
Precautions |
| History of vestibular or auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
Pre-existing significant auditory impairment (hearing loss or tinnitus) |
| History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to an aminoglycoside (rare) |
Pre-existing vestibular condition (dizziness, vertigo or balance problems) |
| Myasthenia gravis |
Family history (first-degree relative) of auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
- A single dose can be used in patients with:
- Chronic renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min) or rapidly deteriorating
renal function
- Advanced age (eg 80 years or older), depending on calculated renal function
- If you are unsure whether gentamicin is appropriate for this patient please consult infectious
diseases
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below)
Diagnostic Criteria for Penicillin Allergy:
- Non-life threatening reactions such as minor rash, skin irritation, nausea, diarrhoea or vomiting
should not usually be considered life threatening and may not be an allergic reaction at all
- There is only a 2.5% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient previously allergic to penicillin.
In most cases it is safe to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life
threatening reaction to penicillin
- Life-threatening reactions include SJS, DRESS, TENS or any reaction that led to respiratory
compromise
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below)
Diagnostic Criteria for Penicillin Allergy:
- Non-life threatening reactions such as minor rash, skin irritation, nausea, diarrhoea or vomiting
should not usually be considered life threatening and may not be an allergic reaction at all
- There is only a 2.5% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient previously allergic to penicillin.
In most cases it is safe to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life
threatening reaction to penicillin
- Life-threatening reactions include SJS, DRESS, TENS or any reaction that led to respiratory
compromise
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Urological surgery
Is gentamicin contraindicated in this patient?
(See below)
Aminoglycoside Contraindications and Precautions
| Contraindications |
Precautions |
| History of vestibular or auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
Pre-existing significant auditory impairment (hearing loss or tinnitus) |
| History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to an aminoglycoside (rare) |
Pre-existing vestibular condition (dizziness, vertigo or balance problems) |
| Myasthenia gravis |
Family history (first-degree relative) of auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
- A single dose can be used in patients with:
- Chronic renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min) or rapidly deteriorating
renal function
- Advanced age (eg 80 years or older), depending on calculated renal function
- If you are unsure whether gentamicin is appropriate for this patient please consult infectious
diseases
Surgical prophylaxis
For open or laparoscopic urological procedures:
Gentamicin (adult and child) 2 mg/kg IV, within 120 minutes
before surgical incision.
AND
Metronidazole 500 mg (child 1 month or older: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500
mg) IV, 12-hourly
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
- If there is untreated bacteruria the gentamicin dose should be increased to 3mg/kg
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Urological surgery
Is the patient known to be, or at risk of colonisation with MRSA?
Surgical prophylaxis
For open or laparoscopic urological procedures:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Trimethoprim+sulfamethoxazole 160+800 mg (child 1 month or older:
4+20 mg/kg up to 160+800 mg) orally, within 30 minutes before surgical incision
OR
Trimethoprim 300 mg orally, within 30 minutes before surgical
incision
- If there is a risk of entry into the bowel lumen (eg ileal conduit, rectoceale repair) then
add metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within 30 minutes of surgical
incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
For open or laparoscopic urological procedures where gentamicin is
contraindicated and patient has MRSA infection:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Cefazolin 2 g (child or adult < 40kg: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV,
within 60 minutes before surgical incision.
AND
Trimethoprim+sulfamethoxazole 160+800 mg (child 1 month or older:
4+20 mg/kg up to 160+800 mg) orally, within 30 minutes before surgical incision
- If there is a risk of entry into the bowel lumen (eg ileal conduit, rectoceale repair) then
add metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within 30 minutes of surgical
incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
For open or laparoscopic urological procedures where gentamicin is
contraindicated:
Cefazolin 2 g (child or adult < 40kg: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV,
within 60 minutes before surgical incision.
AND
Trimethoprim+sulfamethoxazole 160+800 mg (child 1 month or older:
5+25 mg/kg up to 160+800 mg) orally, within 30 minutes before surgical incision
OR
Trimethoprim 300 mg orally, within 30 minutes before surgical
incision
- If there is a risk of entry into the bowel lumen (eg ileal conduit, rectoceale repair) then
add metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within 30 minutes of surgical
incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Urological surgery
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below)
Diagnostic Criteria for Penicillin Allergy:
- Non-life threatening reactions such as minor rash, skin irritation, nausea, diarrhoea or vomiting
should not usually be considered life threatening and may not be an allergic reaction at all
- There is only a 2.5% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient previously allergic to penicillin.
In most cases it is safe to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life
threatening reaction to penicillin
- Life-threatening reactions include SJS, DRESS, TENS or any reaction that led to respiratory
compromise
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Surgical prophylaxis
For open or laparoscopic urological procedures:
Gentamicin (adult and child) 2 mg/kg IV, within 120 minutes
before surgical incision.
AND either
① Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120
minutes before surgical incision (recommended rate 10 mg/min)
OR
① Clindamycin 600mg IV, started within
the 120 minutes before the procedure
- If there is a risk of entry into the bowel lumen (eg ileal conduit, rectoceale repair) then
add metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within 30 minutes of surgical
incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
- If there is untreated bacteruria the gentamicin dose should be increased to 3mg/kg
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
For open or laparoscopic urological procedures:
Cefazolin 2 g (child or adult < 40kg: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV,
within 60 minutes before surgical incision
AND
Gentamicin (adult and child) 2 mg/kg IV, within 120 minutes
before surgical incision.
- If there is a risk of entry into the bowel lumen (eg ileal conduit, rectoceale repair) then
add metronidazole 500 mg (child: 12.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg) IV, within 30 minutes of surgical
incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
- If there is untreated bacteruria the gentamicin dose should be increased to 3mg/kg
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
Is surgical prophylaxis required?
- For ERCP surgical prophylaxis is not required for:
- ERCP with evidence of biliary tract obstruction if complete biliary drainage is likely to be
achieved
- Other ERCP procedures if the patient does not have communicating pancreatic cysts or pseudocysts
- For ERCP surgical prophylaxis is required for:
- ERCP involving transpapillary or transmural drainage of pseudocyst
- ERCP with evidence of biliary tract obstruction ONLY IF complete biliary drainage may not be
achieved
- other ERCP procedures ONLY if the patient has communicating pancreatic cysts or pseudocysts
- If the patient is already on antibiotics, surgical prophylaxis is not required if:
- The antimicrobial matches the surgical prophylaxis regimen
- Less than two half lives passed since the antibiotic was last administered (see antibiotic half lives table)
- And surgery is expected to finish within 2 half lives of the antibiotic (see antibiotic half lives table)
(If prophylyaxis is needed) Is gentamicin contraindicated in this
patient?
(See below)
Aminoglycoside Contraindications and Precautions
| Contraindications |
Precautions |
| History of vestibular or auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
Pre-existing significant auditory impairment (hearing loss or tinnitus) |
| History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to an aminoglycoside (rare) |
Pre-existing vestibular condition (dizziness, vertigo or balance problems) |
| Myasthenia gravis |
Family history (first-degree relative) of auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
- A single dose can be used in patients with:
- Chronic renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min) or rapidly deteriorating
renal function
- Advanced age (eg 80 years or older), depending on calculated renal function
- If you are unsure whether gentamicin is appropriate for this patient please consult infectious
diseases
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient with contraindications to gentamicin
use:
Trimethoprim+sulfamethoxazole 160+800 mg (child 1 month or older:
5+25 mg/kg up to 160+800 mg) orally, within 60 minutes before procedure.
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient with no gentamicin contraindications
use:
Gentamicin (adult and child) 2 mg/kg IV, within 120 minutes
before surgical incision.
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
- If there is untreated bacteruria the gentamicin dose should be increased to 3mg/kg
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Is the patient known to be, or at risk of colonisation with MRSA?
(See below)
Risk factors for MRSA colonisation are:
- Risk factors for MRSA infection include: residence in a jail or detention centre, indigenous
heritage, previous MRSA colonisation which has not been cleared, hospital stay for > 5 days
immediately prior to surgery
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Surgical prophylaxis
Does the patient have a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to
penicillin or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient with life-threatening penicillin
reaction/anaphylaxis use:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
AND
Trimethoprim+sulfamethoxazole 160+800 mg (child 1 month or older:
5+25 mg/kg up to 160+800 mg) IV, within 30 minutes before surgical incision.
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient with life-threatening penicillin
reaction/anaphylaxis use as a single agent:
Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV, within 15-120 minutes before surgical incision
(recommended rate 10 mg/min)
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient without life-threatening penicillin
reaction/anaphylaxis or cephalosporin allergy:
Cefazolin 2 g (child or adult <40kg: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV,
within 60 minutes before surgical incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Is the patient known to be, or at risk of colonisation with MRSA?
(See below)
Risk factors for MRSA colonisation are:
- Risk factors for MRSA infection include: residence in a jail or detention centre, indigenous
heritage, previous MRSA colonisation which has not been cleared, hospital stay for > 5 days
immediately prior to surgery
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Surgical prophylaxis
Does the patient have a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to
penicillin or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Appendicitis
Is gentamicin contraindicated in this patient?
(See below for contraindications)
Aminoglycoside Contraindications and Precautions
| Contraindications |
Precautions |
| History of vestibular or auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
Pre-existing significant auditory impairment (hearing loss or tinnitus) |
| History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to an aminoglycoside (rare) |
Pre-existing vestibular condition (dizziness, vertigo or balance problems) |
| Myasthenia gravis |
Family history (first-degree relative) of auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
- A single dose can be used in patients with:
- Chronic renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min) or rapidly deteriorating
renal function
- Advanced age (eg 80 years or older), depending on calculated renal function
- If you are unsure whether gentamicin is appropriate for this patient please consult infectious
diseases
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient with life-threatening penicillin
reaction/anaphylaxis use as a single agent:
Clindamycin 600 mg (child:15 mg/kg up to 600 mg) IV, within 120
minutes before surgical incision
AND
Gentamicin 2 mg/kg IV, over 3-5 minutes, within 120 minuted before
surgical incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Recommended surgical prophylaxis
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient without life-threatening penicillin
reaction/anaphylaxis or cephalosporin allergy:
Cefazolin 2 g (child or adult <40kg: 50 mg/kg up to 2 g) IV,
within 60 minutes before surgical incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Recommended surgical prophylaxis for opthalmic procedures
For surgical prophylaxis in a patient without life-threatening penicillin
reaction/anaphylaxis use:
Cefazolin 1 mg intracamerally, as a single dose at the end of
surgery
AND if postoperative topical antibiotics are considered necessary
chloramphenicol 0.5% eye drops, 1 drop into the operated eye, four times
a day for a maximum of 7 days
Please contact infectious diseases for advice if patient is allergic to
cefazolin or has severe immediate or delayed hypersensitivity to penicillin
- Tobramycin eye drops should only be considered for patients hypersensitive to chloramphenicol but
this does not have activity against Gram-positive organisms
- Active conjunctivitis, dacryocystitis or blepharitis must be treated and resolved before surgery.
- Prevention of endophthalmitis involves a combination of preoperative screening, antisepsis,
intraoperative techniques, and postoperative patient care.
- Antibiotics (particularly vancomycin) in irrigation solutions should not be used
- There is a lack of evidence to support use of topical quinolones, seek expert advice if topical
quinolones are deemed necessary
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
Has the patient had a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis to penicillin
or a cephalosporin allergy?
(See below for details on penicillin allergy severity)
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Minor penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Anaphylaxis/life-threatening reaction
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) and other life-threatening reactions such as
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with
eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
Vascular surgery
Is the patient known to be, or at risk of colonisation with MRSA?
(See below)
Risk factors for MRSA colonisation are:
- Risk factors for MRSA infection include: residence in a jail or detention centre, indigenous
heritage, previous MRSA colonisation which has not been cleared, hospital stay for > 5 days
immediately prior to surgery
Surgical prophylaxis
Is gentamicin contraindicated in this patient?
(See below for contraindications)
Aminoglycoside Contraindications and Precautions
| Contraindications |
Precautions |
| History of vestibular or auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
Pre-existing significant auditory impairment (hearing loss or tinnitus) |
| History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to an aminoglycoside (rare) |
Pre-existing vestibular condition (dizziness, vertigo or balance problems) |
| Myasthenia gravis |
Family history (first-degree relative) of auditory toxicity caused by an aminoglycoside |
- A single dose can be used in patients with:
- Chronic renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min) or rapidly deteriorating
renal function
- Advanced age (eg 80 years or older), depending on calculated renal function
- If you are unsure whether gentamicin is appropriate for this patient please consult infectious
diseases
Surgical prophylaxis
For surgery in a patient with a life threatening reaction/anaphylaxis to
penicillin without MRSA risk factors use:
Gentamicin (adult and child) 2 mg/kg IV, within 120 minutes
before surgical incision
AND
Clindamycin 600 mg (child:15 mg/kg up to 600 mg) IV, within 120
minutes before surgical incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
- Postoperative antibiotic doses can be considered for up to a maximum of 24 hours for patients
undergoing laryngectomy
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Surgical prophylaxis
For surgery in a patient with a life threatening reaction/anaphylaxis to
penicillin without MRSA risk factors use:
Benzylpenicillin 1.2 g (child >1 month 30 mg/kg to a maximum of
1.2 g) IV, within the 60 minutes before surgical incision
- If surgery is prolonged for more than 3 hours see the surgical
prophylaxis antibiotic half life nomogram for details on when to redose antibiotics
- A repeat intra-operative dose may also be required if there is excessive blood loss during the
procedure
- Postoperative doses of antibiotics are only required in defined circumstances (eg some cardiac
and vascular surgeries, laryngectomy, total knee arthroplasty and lower limb amputation).
Prophylaxis should not continue beyond 24 hours regardless of the surgical procedure
- Postoperative antibiotic doses can be considered for up to a maximum of 24 hours for maxillofacial
surgery
References:
See section on surgical prophylaxis - Antibiotic Expert Groups. Therapeutic
guidelines: antibiotic. Version 15. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2019.
Water Immersed Wound
Does the patient have an active infection or a wound at high risk of infection?
See below for details
Antibiotic prophylaxis is only required for water exposed injuries with
established infection or a high risk of infection such as:
- Wounds with delayed presentation for washout (8 hours or more)
- Puncture wounds which can not be debrided adequately
- Wounds on the hands feet or face
- Wounds involving deeper tissues (eg. bones, joints, tendons)
- Wounds in immunocompromised patients
- Wounds which also involve an open fracture (see open fracture section)
- Risk factors for severe disease such as; liver disease, iron overload, immune compromise due to immunosuppressive medications, diabetes or malignancy
Water Immersed Wound
Was the wound exposed to fresh or salt water?
See below for details
Antibiotic prophylaxis is only required for water exposed injuries with
established infection or a high risk of infection such as:
- Wounds with delayed presentation for washout (8 hours or more)
- Puncture wounds which can not be debrided adequately
- Wounds on the hands feet or face
- Wounds involving deeper tissues (eg. bones, joints, tendons)
- Wounds in immunocompromised patients
- Wounds which also involve an open fracture (see open fracture section)
- Risk factors for severe disease such as; liver disease, iron overload, immune compromise due to immunosuppressive medications, diabetes or malignancy
Pyelonephritis
Does the patient have a penicillin allergy?
See below for details on penicillin allergy severity
History of penicillin allergy or adverse reaction
No penicillin allergy
- This includes non-severe reactions such as nausea and limited diarrhoea
- Such reactions are frequently not replicable or generalizable to the whole class. It is safe to
prescribe penicillin class antibiotics (with the patient’s knowledge), and if required, use
strategies for symptom control such as metoclopramide
Non-severe immediate or delayed penicillin hypersensitivity
- This includes non-severe reactions such as isolated rash
- There is only a 2-3% chance of cephalosporin allergy in a patient with a previous IgE mediated
allergy to penicillin, and probably even less for other types of allergies. In most cases it is safe
to administer a cephalosporin to a patient who has had a non-life threatening reaction to penicillin
Severe immediate or delayed penicillin hypersensitivity
- This includes anaphylaxis (see below) BUT DOES NOT INCLUDE other life-threatening reactions
such as Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug
reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or interstitial nephritis. If your
patient has a history of these, contact infectious diseases for advice
Penicillin anaphylaxis is highly likely if any ONE of the following is fulfilled:
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours)
involving the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalised hives, pruritus or flushing,
swollen lips-tongue-uvula) and at least one of:
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze/bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
OR
- Reduced blood pressure (BP) or associated symptoms and signs of end-organ
malperfusion (eg, hypotonia [collapse] syncope, incontinence)
OR
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly
after exposure to penicillin for that patient (within minutes to several hours):
- Involvement of the skin-mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen
lips-tongue-uvula)
- Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, reduced peak
expiratory flow, hypoxemia)
- Reduced BP or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia [collapse], syncope,
incontinence)
- Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and signs (eg, crampy abdominal pain,
vomiting)
OR
3. Reduced BP after exposure to penicillin in a patient
with known penicillin allergy (within minutes to several hours)
- Reduced BP in adults is defined as a systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30
percent decrease from that person's baseline
- In infants and children, reduced BP is defined as low systolic BP (age-specific)
or greater than 30 percent decrease in systolic BP
- i.e. Less than 70 mmHg from 1 month up to 1 year
- Less than (70 mmHg + [2 x age]) from 1 to 10 years
- Less than 90 mmHg from 11 to 17 years
